Cryptocurrency scams are unfortunately quite common, given the digital and often anonymous nature of crypto transactions. Here are some of the most prevalent types of cryptocurrency scams:
-
Phishing Scams: These scams involve tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information such as private keys or wallet passwords. Scammers might create fake websites or send emails that mimic legitimate cryptocurrency services to steal users’ information.
-
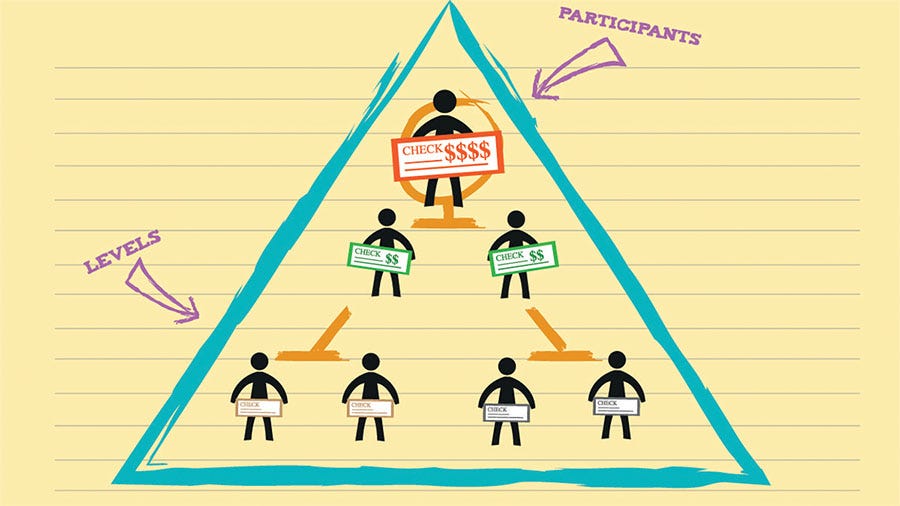
Ponzi and Pyramid Schemes: These schemes promise high returns to investors for doing little to no work. In reality, returns are paid to earlier investors using the capital from newer investors, and the scheme collapses once there aren’t enough new investors.
-
Fake ICOs (Initial Coin Offerings): Scammers create fake ICOs to lure investors into investing in non-existent or fraudulent projects. They often use elaborate marketing campaigns and false promises of high returns.
-
Pump and Dump Schemes: These involve artificially inflating the price of a lesser-known cryptocurrency (the “pump”) through misleading positive statements. Once the price is high enough, scammers sell off their holdings (the “dump”), causing the price to plummet and leaving other investors with worthless assets.
-
Impersonation and Fake Endorsements: Scammers impersonate celebrities, well-known crypto personalities, or legitimate crypto projects, often on social media, to promote scams. They may also create fake endorsements to add credibility to their schemes.
-
Ransomware and Malware: Malicious software is used to take control of a victim’s computer or mobile device, demanding a ransom, often in cryptocurrency, to restore access or not release sensitive information.
-
Romance Scams: In these scams, the scammer builds a romantic relationship with the victim and eventually persuades them to send money in cryptocurrency under various pretexts.
-
Giveaway Scams: Scammers promise to multiply cryptocurrency sent to them as part of a giveaway or competition. However, once the cryptocurrency is sent, the scammer disappears with the funds.
-
Exchange and Wallet Scams: Some fake platforms pose as legitimate cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets. After users deposit funds, they find they can’t withdraw their money or the platform shuts down suddenly.
-
Non-Existent or Fraudulent NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens): With the rise of NFTs, there’s been an increase in scams involving fake or plagiarized NFTs being sold as authentic or valuable.
“The first step toward avoiding scams is to learn how to spot them.”
Awareness and vigilance are crucial in the cryptocurrency space to avoid falling victim to these scams. Always research thoroughly, use reputable services, and be wary of offers that sound too good to be true.